Lighthouse: Efficiently encode images
Overview
When looking at your page requests, images likely account for the bulk of your total page size compared to HTML, CSS, or JavaScript files.
If these images are uncompressed, they waste bandwidth and increase page load times because the browser must spend more time downloading them.
Efficiently encoding images reduces your page size and contributes to a faster loading page.
How does your site score on this audit?
How does efficiently encoding images affect page performance?
Uncompressed images are likely served at very high quality, resulting in a large file size.
The larger the image, the more time the browser spends downloading them, further increasing the time your visitors spend waiting for the page to load.
When this happens for multiple images on your page, the file sizes can add up significantly and result in a very slow page.
Efficiently encoding images i.e., serving compressed images, can reduce image file sizes and speed up image downloads for an ultimately faster loading page.

There are 2 types of compression algorithms commonly used, namely:
- Lossy compression - reduces file sizes at the expense of image quality.
- Lossless compression - reduces file sizes without sacrificing quality.
To learn more, read our What does image optimization mean? article.
How does GTmetrix trigger this audit?
GTmetrix evaluates all the JPEG and BMP images on your page and compresses them to 85% of their original quality.
If the compressed image is at least 4KB smaller than the original image, it is flagged. Clicking the audit on the GTmetrix report lists the relevant images.
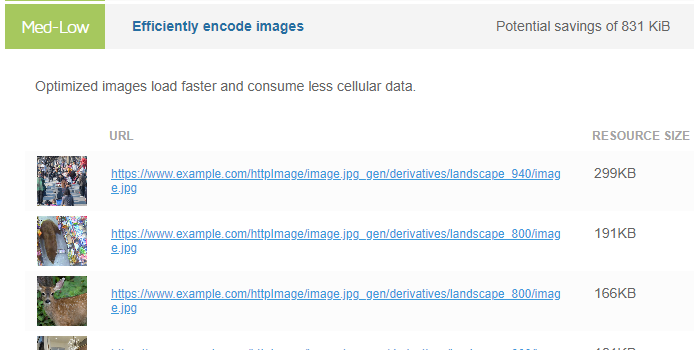
GTmetrix also estimates the file size savings that could be achieved through serving compressed images.
How to efficiently encode images?
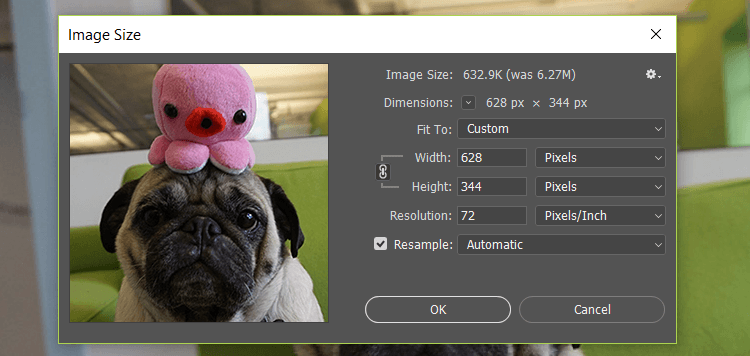
There are a few strategies to efficiently encode images, such as:1) Manually compressing images
We've previously written a Practical Guide on How to Optimize Images, which highlights the manual method to compress your images.
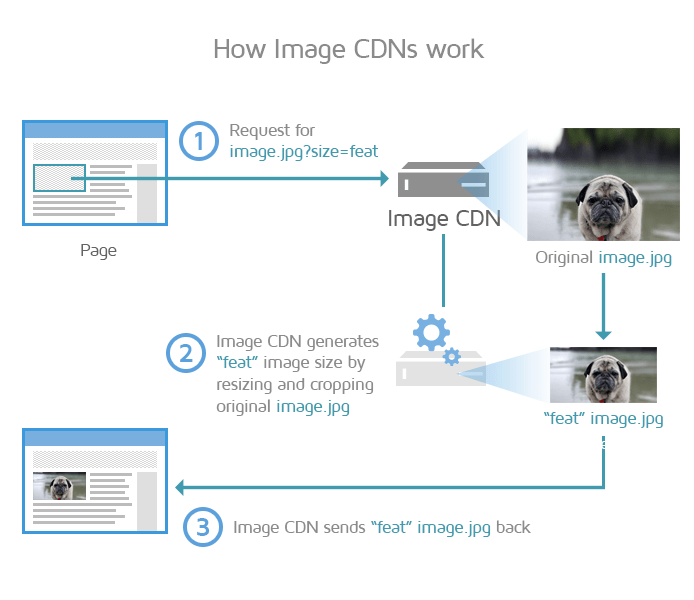
2) Using an Image CDN
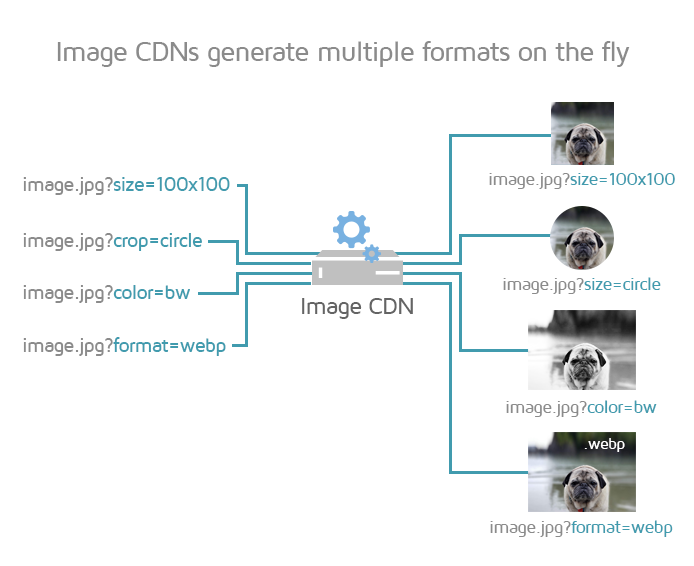
You can use an Image CDN to serve images that are optimally compressed, resized to the visitor's viewport, and served from the closest geographic location to your visitor.
A bonus is that you do not need to build image optimization practices into your development workflow, as the Image CDN can handle all things image-related on your production websites.
Read more about Image CDNs here.
3) Using CMS Plugins (For WordPress or other CMS)
CMS users (e.g., WordPress, Shopify, etc.) can use a plugin to compress and optimize image delivery.
For example, Imagify offers bulk and on-upload image optimization for WordPress users.
Click here to learn more about optimizing images for WordPress.